A mempool (short for “memory pool”) is a crucial component of a blockchain network, where unconfirmed transactions are stored after they are broadcasted by users. It is a temporary storage area in a node where unconfirmed transactions are kept before they are added to a block. When a user initiates a transaction, it is broadcasted to all the nodes in the network. Nodes validate the transaction and, if it’s valid, add it to their mempool. The transaction remains in the mempool until it is confirmed and added to a block by a miner.
How does the Mempool work?
Mempool works by allowing nodes to keep track of unconfirmed transactions until they are confirmed by a miner. The mempool constantly changes as new transactions are added, confirmed transactions are removed, and unconfirmed transactions are dropped. Transactions with higher fees attached to them are prioritized by miners, as they have an incentive to include transactions with higher fees in order to earn more rewards. Transactions with low fees may eventually be dropped from the mempool if they remain unconfirmed for too long, and the funds will be returned to your wallet. Some bitcoin wallets have a replace by fee (RBF) feature that allows you to replace a low-fee transaction with a new one with a higher fee to speed up your transaction.
The length of time it takes for a transaction to be dropped from the mempool can vary depending on several factors, including the network’s congestion level and the fee attached to the transaction. Bitcoin nodes typically drop transactions from their mempools after they have been unconfirmed for about 14 days.
Find out more: What’s a replace by fee (RBF)?
Benefits of the Mempool
The mempool offers several benefits to a blockchain network. Firstly, it allows nodes to validate transactions before they are confirmed, helping prevent double-spending. Secondly, it allows miners to select which transactions to include in new blocks, prioritizing those with higher fees attached. This incentivizes users to attach higher fees to their transactions to ensure that they are processed quickly. Finally, the mempool can help prevent network congestion by limiting the number of unconfirmed transactions that are processed at once.
Drawbacks of the Mempool
The mempool does have some drawbacks. The main issue is that it can be a target for spam attacks, where bad actors flood the network with fake transactions to clog up the mempool and slow down the network. Additionally, some users may attempt to exploit the mempool by attaching low fees to their transactions to try and force miners to prioritize their transactions over others, potentially slowing down the network.
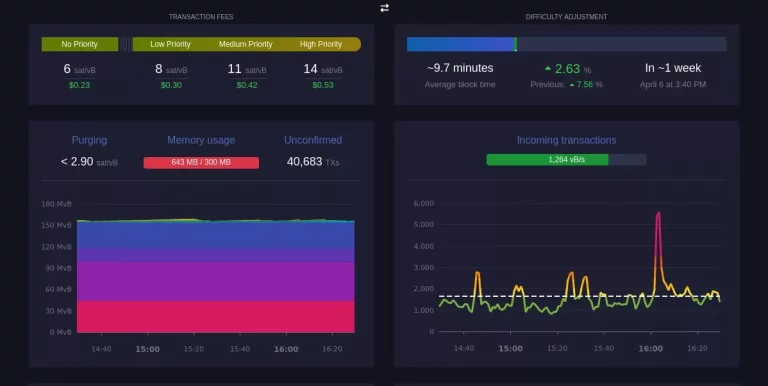
How to view the Mempool
You can take a look at the mempool of a blockchain network using various tools and resources. Here are a few ways to do it:
- Blockchain explorer: Many blockchain explorers, such as Blockchain.com for bitcoin provide a real-time view of the network’s mempool. These tools allow you to see all the unconfirmed transactions waiting to be added to the blockchain.
- Network monitoring tools: There are several network monitoring tools available that allow you to see the mempool data in real-time. Some popular tools include Mempool Observer and Mempool.Space.
- Node software: If you are running a full node of a blockchain network, you can access the mempool data directly from the node software. Most node software, such as Bitcoin Core allow you to access the mempool data and see all the unconfirmed transactions waiting to be processed.
It’s important to note that the mempool data can be quite large and complex, especially for popular blockchain networks like Bitcoin. However, by using these tools and resources, you can get a better understanding of how the mempool works and see the current state of the network’s unconfirmed transactions.
The mempool is a crucial component of any blockchain network. It allows nodes to keep track of unconfirmed transactions and miners to select which transactions to include in new blocks. It is essential to the functioning of a blockchain network and helps ensure the integrity and security of the network.